Definition and Calculation of Duty Cycle
– Duty cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active.
– It is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio.
– The duty cycle (%) can be calculated as the pulse width (PW) divided by the total period (T), multiplied by 100%.
– The duty cycle (ratio) can be calculated as the pulse width (PW) divided by the total period (T).
– A 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time and off 40% of the time.
Applications in Electrical and Electronics
– In electronics, duty cycle represents the time duration of a pulse when it is high in a rectangular waveform.
– Signals in digital electronics are represented by logic 1 (presence of an electric pulse) and logic 0 (absence of an electric pulse).
– Electrical motors typically use a duty cycle less than 100%.
– Pulse-width modulation (PWM) is used for power delivery and voltage regulation.
– In electronic music, duty cycle variation is used to achieve subtle effects on tone colors.
Applications in Biological Systems
– Duty cycle is used to describe the activity of neurons and muscle fibers in neural circuits.
– It specifically refers to the proportion of a cycle period in which a neuron remains active.
– Duty cycle is used to describe the firing of action potentials by living systems such as neurons.
– It helps in understanding the behavior and functioning of biological systems.
– The concept of duty cycles is important in studying neural circuits and their dynamics.
Generation of Square Wave Signals
– Varying the duty cycle can generate square wave signals with a specific duty factor.
– The duty factor is varied until a specific harmonic is significantly suppressed.
– For audio-band signals, the duty factor can be adjusted by ear to achieve desired reductions in harmonics.
– Precision in duty factor adjustments determines the accuracy of the generated square wave signals.
– This technique is useful in various applications, including audio and telecommunications.
Mark-Space Ratio
– Mark-space ratio is another term for duty cycle and describes the temporal relationship between two alternating periods of a waveform.
– It relates the durations of the two individual periods, on and off.
– The mark-space ratio is calculated as the duration of the on period divided by the duration of the off period.
– It provides information about the relative lengths of the on and off periods in a waveform.
– The mark-space ratio is used in various fields, including telecommunications and electronics. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Duty_cycle
A duty cycle or power cycle is the fraction of one period in which a signal or system is active. Duty cycle is commonly expressed as a percentage or a ratio. A period is the time it takes for a signal to complete an on-and-off cycle. As a formula, a duty cycle (%) may be expressed as:
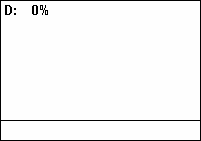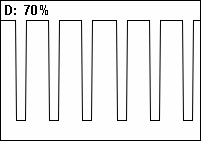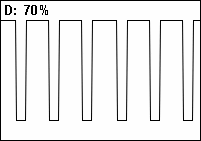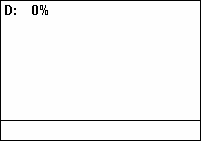
Equally, a duty cycle (ratio) may be expressed as:
where is the duty cycle, is the pulse width (pulse active time), and is the total period of the signal. Thus, a 60% duty cycle means the signal is on 60% of the time but off 40% of the time. The "on time" for a 60% duty cycle could be a fraction of a second, a day, or even a week, depending on the length of the period.
Duty cycles can be used to describe the percent time of an active signal in an electrical device such as the power switch in a switching power supply or the firing of action potentials by a living system such as a neuron.
Some publications use as the symbol for duty cycle.
As a ratio, duty cycle is unitless and may be given as decimal fraction and percentage alike.
An alternative term in use is duty factor.






