Introduction to Diodes:
– A diode is a type of electronic component.
– It is a passive device used in various electronic circuits.
– Diodes allow electric current to flow in only one direction.
– They are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon.
– Diodes have two terminals: the anode and the cathode.
Types of Diodes:
– Rectifier diodes are used to convert AC to DC.
– Zener diodes are used for voltage regulation.
– Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) emit light when current passes through them.
– Schottky diodes have a low forward voltage drop.
– Photodiodes are used to detect light and convert it into electrical current.
Operation of Diodes:
– Diodes have a forward bias and a reverse bias.
– In forward bias, the anode is at a higher voltage than the cathode.
– This allows current to flow through the diode.
– In reverse bias, the cathode is at a higher voltage than the anode.
– This blocks current flow through the diode.
Applications of Diodes:
– Diodes are used in power supplies to convert AC to DC.
– They are used in voltage regulators to stabilize voltage levels.
– Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are used in various lighting applications.
– Diodes are used in solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity.
– They are used in communication systems for signal detection and modulation.
Advantages and Limitations of Diodes:
– Diodes are small in size and have a long lifespan.
– They have low power consumption and high efficiency.
– Diodes can handle high current and voltage levels.
– However, diodes have a voltage drop and can generate heat.
– They are sensitive to reverse voltage and can be damaged if not used correctly. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance). It has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
 Close-up view of a silicon diode. The anode is on the right side; the cathode is on the left side (where it is marked with a black band). The square silicon crystal can be seen between the two leads. | |
| Type | Passive |
|---|---|
| Pin configuration | Anode and cathode |
| Electronic symbol | |
 | |

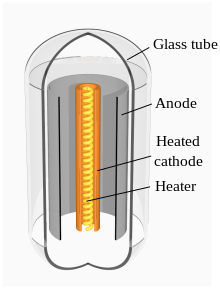
A semiconductor diode, the most commonly used type today, is a crystalline piece of semiconductor material with a p–n junction connected to two electrical terminals. It has an exponential current–voltage characteristic. Semiconductor diodes were the first semiconductor electronic devices. The discovery of asymmetric electrical conduction across the contact between a crystalline mineral and a metal was made by German physicist Ferdinand Braun in 1874. Today, most diodes are made of silicon, but other semiconducting materials such as gallium arsenide and germanium are also used.
The obsolete thermionic diode is a vacuum tube with two electrodes, a heated cathode and a plate, in which electrons can flow in only one direction, from cathode to plate.
Among many uses, diodes are found in rectifiers to convert alternating current (AC) power to direct current (DC), demodulation in radio receivers, and can even be used for logic or as temperature sensors. A common variant of a diode is a light-emitting diode, which is used as electric lighting and status indicators on electronic devices.
