Overview of CAD
– CAD is a tool used by engineers and designers in various professions.
– CAD is part of digital product development (DPD) within product lifecycle management (PLM) processes.
– CAD is used together with other tools such as computer-aided engineering (CAE) and finite element analysis (FEA).
– CAD is also used for computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) and photorealistic rendering.
– CAD is used for document management and revision control using product data management (PDM).
Types of CAD
– There are several different types of CAD.
– CAD tools rely on constraint concepts to define elements of a model.
– 2D CAD systems allow easy adjustment of scale and placement on the drawing sheet.
– 3D CAD systems extend 2D drafting into a three-dimensional space.
– 3D CAD systems can create wireframe models or dumb solids.
2D CAD
– Lower-end 2D sketching systems are available, including free and open-source programs.
– Scale and placement on the drawing sheet can be easily adjusted.
– 2D CAD allows for easy modifications in the final draft.
– Hand drafting techniques are not required.
– 2D CAD is commonly used for accurate creation of photo simulations.
3D CAD
– 3D CAD extends 2D drafting into a three-dimensional space.
– Lines need to be manually inserted into the drawing.
– 3D CAD models have no mass properties and cannot have features directly added.
– Final engineering drawing views can be generated from the wireframe model.
– 3D CAD systems allow the creation of 3D dumb solids with added or subtracted volumes.
Technology and Evolution of CAD
– CAD software was initially developed using languages like Fortran and ALGOL.
– Object-oriented programming languages are now commonly used for CAD software.
– Top-end CAD systems offer the capability to incorporate organic and aesthetic features.
– Freeform surface modeling is often combined with solids for ergonomic designs.
– Advanced CAD systems can handle complex models in building engineering.
– IBM Drafting System introduced in the mid-1960s.
– CAD systems provided more capabilities than electronic drafting.
– Automated tasks such as bill of materials generation and interference checking.
– CAD merged the roles of draftsman, designer, and engineer.
– Modern CAD packages range from 2D drafting to 3D solid and surface modeling. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computer-aided_design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (orworkstations) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve communications through documentation, and to create a database for manufacturing. Designs made through CAD software help protect products and inventions when used in patent applications. CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations. The terms computer-aided drafting (CAD) and computer-aided design and drafting (CADD) are also used.
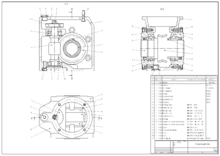
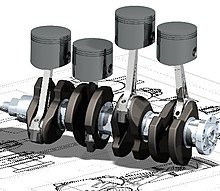
Its use in designing electronic systems is known as electronic design automation (EDA). In mechanical design it is known as mechanical design automation (MDA), which includes the process of creating a technical drawing with the use of computer software.
CAD software for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics to depict the objects of traditional drafting, or may also produce raster graphics showing the overall appearance of designed objects. However, it involves more than just shapes. As in the manual drafting of technical and engineering drawings, the output of CAD must convey information, such as materials, processes, dimensions, and tolerances, according to application-specific conventions.
CAD may be used to design curves and figures in two-dimensional (2D) space; or curves, surfaces, and solids in three-dimensional (3D) space.
CAD is an important industrial art extensively used in many applications, including automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, industrial and architectural design (building information modeling), prosthetics, and many more. CAD is also widely used to produce computer animation for special effects in movies, advertising and technical manuals, often called DCC digital content creation. The modern ubiquity and power of computers means that even perfume bottles and shampoo dispensers are designed using techniques unheard of by engineers of the 1960s. Because of its enormous economic importance, CAD has been a major driving force for research in computational geometry, computer graphics (both hardware and software), and discrete differential geometry.
The design of geometric models for object shapes, in particular, is occasionally called computer-aided geometric design (CAGD).
