Circuit Diagram Symbols and Organization
– Circuit diagrams use standardized symbols internationally.
– Symbols for components have changed over time.
– The resistor symbol used to represent a long piece of wire.
– Wire crossover symbols indicate insulated crossing wires.
– Modern practice for representing 4-way wire connection is to use T-junctions.
– Schematic drawings are usually organized from left to right and top to bottom.
– Signal flow follows the sequence of the main signal or power path.
– Positive power supply connections are shown towards the top, grounds or negative supplies towards the bottom.
– Maintenance schematics highlight principal signal paths.
– Cross-reference symbols are used in multi-page schematics.
Circuit Diagram Artwork and Education
– Schematic is converted into a layout for fabrication onto a PCB.
– Schematic-driven layout involves schematic capture and results in a rats nest.
– EDA tools are used to route wires and find paths for tracks.
– Final layout artwork is developed for the integrated circuit or PCB.
– Generalized design flow includes schematic capture, routing, PCB development, and testing.
– Electrical circuit functioning is taught in primary and secondary schools.
– Students learn about circuit diagrams and their functioning.
– Diagrammatic representations aid understanding of electricity principles.
– Analogies, such as comparing circuits to water heating systems, are used for teaching.
– Physics principles are taught through the use of circuit diagrams.
Circuit Diagram Usage and Reference Designations
– Circuit diagrams are used for circuit design, construction, and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment.
– They are particularly useful in computer science for visualizing expressions using Boolean algebra.
– Circuit diagrams show actual electrical connections, unlike block or layout diagrams.
– They are labeled with descriptors or reference designators matching the parts list.
– Detailed rules for reference designations are provided in the international standard IEC 61346.
Boxology and Circuit Design Language
– Boxology is a related field to circuit diagrams.
– It involves the study of the physical layout and arrangement of components in a circuit.
– Boxology helps in understanding the overall structure and organization of a circuit.
– It is essential for troubleshooting and maintenance purposes.
– Boxology is often used in conjunction with circuit diagrams to provide a complete understanding of a circuit’s design.
– Circuit design language is a specialized language used to describe circuits.
– It provides a standardized way to represent circuit designs.
– Circuit design languages are used in software tools for circuit design and simulation.
– Examples of circuit design languages include VHDL and Verilog.
– Circuit design languages enable efficient communication and collaboration among circuit designers.
Electronic Symbols, Logic Gates, and Schematic Capture
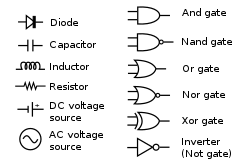
– Electronic symbols are graphical representations of electronic components and devices.
– They are used in circuit diagrams to depict the different components.
– Electronic symbols provide a concise and standardized way to represent components.
– Familiarity with electronic symbols is essential for understanding and interpreting circuit diagrams.
– There are various international standards for electronic symbols, such as the IEC 60617 standard.
– A logic gate is an elementary building block of digital circuits.
– It performs a specific logical operation based on its inputs.
– Logic gates are represented by specific symbols in circuit diagrams.
– Common types of logic gates include AND, OR, NOT, and XOR gates.
– Understanding logic gates is fundamental to designing and analyzing digital circuits.
– Schematic capture is the process of creating a digital representation of a circuit diagram.
– It involves using software tools to draw and connect components in a circuit.
– Schematic capture allows for easy modification and documentation of circuit designs.
– It is an essential step in the electronic design automation (EDA) process.
– Schematic capture enables efficient collaboration and sharing of circuit designs. Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Circuit_diagram
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2009) |
A circuit diagram (or: wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram shows the components and interconnections of the circuit using standardized symbolic representations. The presentation of the interconnections between circuit components in the schematic diagram does not necessarily correspond to the physical arrangements in the finished device.


Unlike a block diagram or layout diagram, a circuit diagram shows the actual electrical connections. A drawing meant to depict the physical arrangement of the wires and the components they connect is called artwork or layout, physical design, or wiring diagram.
Circuit diagrams are used for the design (circuit design), construction (such as PCB layout), and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment.
In computer science, circuit diagrams are useful when visualizing expressions using Boolean algebra.
